요청 본문 처리
1. 라우팅 및 세팅
1.1 URL 정보
이번 챕터의 URL 구성은 아래와 같습니다. 이번에는 앞서 작성했던 URL 정보에 메서드를 추가하였습니다.
| 경로 | 함수명 | 메서드 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
| / | index | GET | 들어온 값을 그대로 출력합니다. |
| /item | item_list | GET | 물품 목록을 반환합니다. |
| /item/{item_id} | item_detail | GET | 물품 상세 정보를 반환합니다. |
| /item/{item_id} | item_update | PUT | 물품 상세 정보를 업데이트합니다. |
| /item | item_create | POST | 물품을 등록합니다. |
1.2 기본 세팅
이번 실습 폴더는 02_3_request입니다. VSC 터미널에서 사용할 명령어 입니다. 가상환경은 벗어난 상태에서 실행해야 합니다. 만약 터미널 입력창 앞에 (venv)라고 되어 있다면 deactivate 명령어로 가상환경을 나간 상태에서 cd ..으로 상위 폴더로 나와 아래 명령어를 실행해주세요.
mkdir 02_3_request
cd 02_3_request
python -m venv venv
.\venv\Scripts\activate
pip install fastapi
pip install uvicornmkdir 02_3_request
cd 02_3_request
python -m venv venv
.\venv\Scripts\activate
pip install fastapi
pip install uvicorn1.3 GET과 POST 요청
GET 요청은 URL로 데이터를 전달하고, POST 요청은 요청 본문에 데이터를 담아 서버로 전송합니다. 아래와 같이 index.html 파일을 만들어주세요. 파일을 만들고 더블 클릭하여 실행해도 되고, VSCode에서 Extension인 Live Server를 설치하여 실행하여도 됩니다.
<form action="" method="GET">
<input type="text" name="name">
<input type="number" name="price">
<button type="submit">제출</button>
</form>
<form action="" method="POST">
<input type="text" name="name">
<input type="number" name="price">
<button type="submit">제출</button>
</form><form action="" method="GET">
<input type="text" name="name">
<input type="number" name="price">
<button type="submit">제출</button>
</form>
<form action="" method="POST">
<input type="text" name="name">
<input type="number" name="price">
<button type="submit">제출</button>
</form>본문에 값을 담아 보낸다는 말이 무엇인가요?
데이터는 서버로 전송할 때 URL에 담아 보낼 수도 있고, 요청 본문에 담아 보낼 수도 있습니다. 실제로 여러분 컴퓨터에서 서버로 보내지는 패킷의 구조, 메서드 등은 아래 네트워크 베이스캠프 자료를 참고해주세요.
POST /api/users HTTP/1.1 # 요청라인(URL로 데이터 요청)
Host: www.example.com # 헤더
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 59
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64)
Accept: application/json
# 빈줄
{"name": "John", "age": 30} # JSON 형식의 본문POST /api/users HTTP/1.1 # 요청라인(URL로 데이터 요청)
Host: www.example.com # 헤더
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 59
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64)
Accept: application/json
# 빈줄
{"name": "John", "age": 30} # JSON 형식의 본문아래와 같은 창에서 첫번째 폼에 값을 넣고 제출 버튼을 누르게 되면 아래와 같은 형식으로 URL이 변경됩니다.
http://127.0.0.1:5500/?name=hello&price=100http://127.0.0.1:5500/?name=hello&price=100이렇게 ? 뒤에 붙은 값들은 GET 요청으로 전달된 값입니다. 현재 form에 action이 비어있기 때문에 현재 페이지로 GET 요청을 보내게 됩니다. 여기 주소를 FastAPI가 서비스 되고 있는 http://localhost:8000/로 변경하면 FastAPI에서 GET 요청을 받을 수 있습니다. GET만 한 번 실습해보도록 하겠습니다.
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
async def index(name: str, price: int):
print(name, price)
return {"name": name, "price": price}from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
async def index(name: str, price: int):
print(name, price)
return {"name": name, "price": price}위 코드를 main.py로 생성한 후 아래 명령어로 실행해주세요.
uvicorn main:app --reloaduvicorn main:app --reload.html코드는 아래와 같이 수정해주세요.
<form action="http://localhost:8000/" method="GET">
<input type="text" name="name">
<input type="number" name="price">
<button type="submit">제출</button>
</form><form action="http://localhost:8000/" method="GET">
<input type="text" name="name">
<input type="number" name="price">
<button type="submit">제출</button>
</form>이제 index.html을 실행하고 값을 입력하고 제출 버튼을 누르면 URL은 http://localhost:8000/?name=hello&price=100와 같이 변하고, 터미널에는 name과 price가 찍히며, 아래와 같은 결과가 나오게 됩니다.
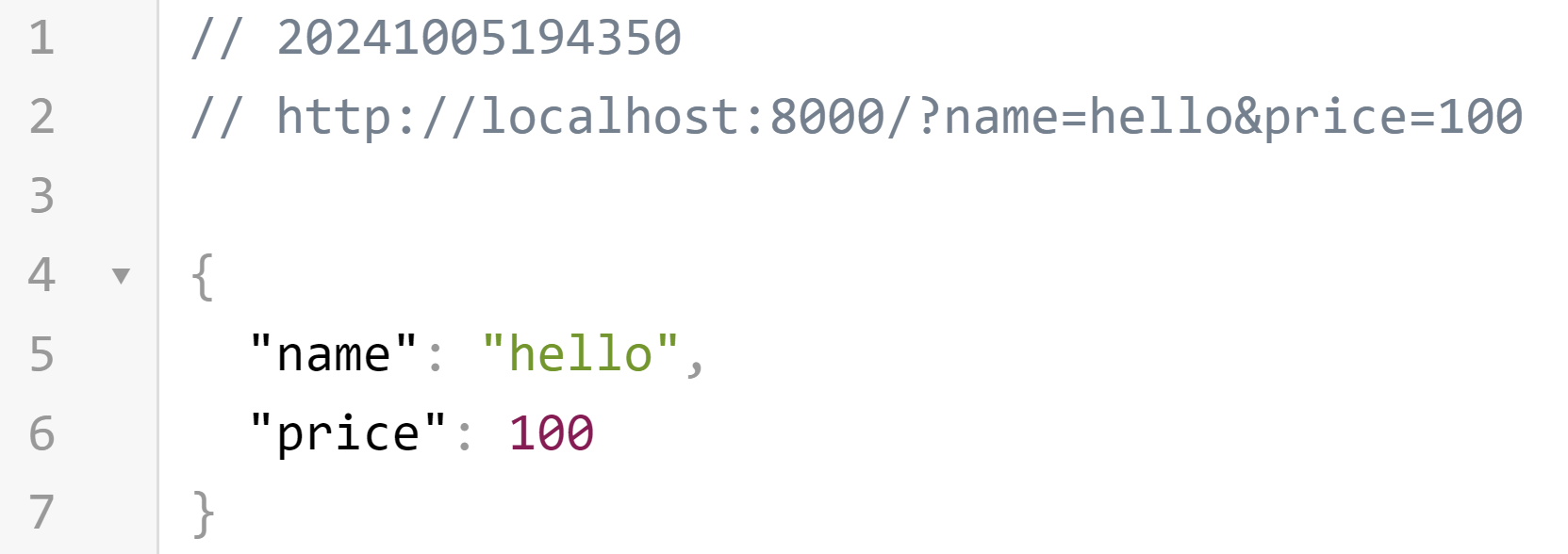
다만 이렇게 실습을 하면 .html파일을 매번 작성해야 하는 번거로움이 있습니다. 이럴 때 Thunder Client를 사용하면 편리합니다. 우리 수업에서는 FastAPI 공부에 좀 더 초점을 맞추기 위해 Thunder Client를 사용하도록 하겠습니다.
이렇게 .html 파일을 만들어도 제대로된 테스트를 할 수 없습니다. CORS 때문인데요. CORS는 미들웨어에서 다룹니다. 따라서 Thunder Client를 사용하는 것은 현재 챕터에서 선택이 아니라 필수 입니다.
2. Thunder Client
Thunder Client는 VSCode의 익스텐션으로, API 테스트를 쉽게 할 수 있도록 도와줍니다. Thunder Client를 사용하면 브라우저를 열고 URL을 입력하지 않더라도, .html 파일을 생성하지 않고도 아래와 같이 GET과 POST 등에 API 테스트를 할 수 있습니다.
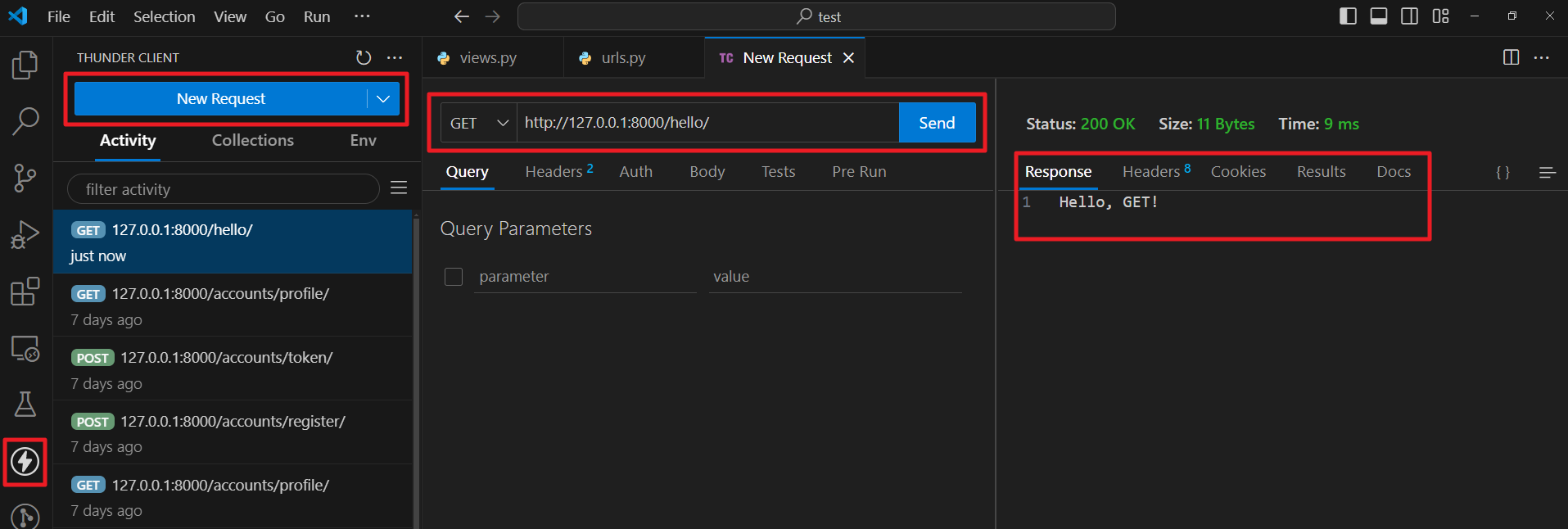
설치는 VSCode의 익스텐션 탭에서 Thunder Client를 검색하여 설치하면 됩니다. 설치가 완료되면 왼쪽 사이드바에 번개모양 아이콘이 생깁니다.
3. POST 요청 처리하기
POST 요청은 서버에 새로운 데이터를 생성하거나 기존 데이터를 수정할 때 주로 사용됩니다. FastAPI에서 POST 요청을 처리하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/item")
async def item_create(item: dict):
return {"item": item}from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/item")
async def item_create(item: dict):
return {"item": item}이 코드는 /item 경로로 들어오는 POST 요청을 처리합니다. item은 요청 본문의 JSON 데이터를 파이썬 딕셔너리로 변환한 것입니다.
Thunder Client를 사용하여 POST 요청을 보내보겠습니다. Thunder Client클릭한 다음 New Request를 클릭하고 POST에 127.0.0.1:8000/item를 입력하고, Body 탭에서 JSON을 선택하고 다음과 같이 입력하세요.
{
"name": "item1",
"price": 100
}{
"name": "item1",
"price": 100
}다음과 같이 응답이 왔다면 정상입니다.
{
"item": {
"name": "item1",
"price": 100
}
}{
"item": {
"name": "item1",
"price": 100
}
}실제로 구동이 되었는지 확인해보기 위해 상품 등록 확인 코드를 추가해보겠습니다.
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
items = []
@app.get("/item")
async def item_list():
return {"items": items}
@app.post("/item")
async def item_create(item: dict):
items.append(item)
return {"item": item}from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
items = []
@app.get("/item")
async def item_list():
return {"items": items}
@app.post("/item")
async def item_create(item: dict):
items.append(item)
return {"item": item}POST로 2개의 아이템을 추가하도록 하겠습니다. Thunder Client를 사용하여 POST 요청을 보내주세요. URL은 127.0.0.1:8000/item이고, Body 탭에서 JSON을 선택하고 다음과 같이 입력하세요.
{
"name": "item1",
"price": 100
}{
"name": "item1",
"price": 100
}{
"name": "item2",
"price": 200
}{
"name": "item2",
"price": 200
}이번에는 Thunder Client에서 GET 요청을 보내보겠습니다. URL은 127.0.0.1:8000/item/ 입니다. 아래와 같은 응답이 왔다면 정상입니다.
{
"items": [
{
"name": "item1",
"price": 100
},
{
"name": "item2",
"price": 1000
}
]
}{
"items": [
{
"name": "item1",
"price": 100
},
{
"name": "item2",
"price": 1000
}
]
}4. Pydantic 모델을 사용한 데이터 검증
Pydantic은 FastAPI와 함께 사용되는 데이터 검증 라이브러리입니다. Pydantic 모델을 사용하면 입력 데이터의 구조와 타입을 명확히 정의하고 자동으로 검증할 수 있습니다.
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
items = []
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
price: float = 0
@app.get("/item")
async def item_list():
return {"items": items}
@app.post("/item")
async def item_create(item: Item):
items.append(item)
return {"item": item}from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
items = []
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
price: float = 0
@app.get("/item")
async def item_list():
return {"items": items}
@app.post("/item")
async def item_create(item: Item):
items.append(item)
return {"item": item}이 예제에서 Item 클래스는 Pydantic 모델입니다. name은 필수 필드이며, price는 선택적 필드입니다. price는 선택적 필드로 설정하기 위해 기본값을 0으로 설정했습니다. 이번에는 Thunder Client를 사용하여 POST 요청을 보낼 때 price에 문자열을 입력해보겠습니다.
127.0.0.1:8000/item에 POST 요청으로, Body 탭에서 JSON을 선택하고 다음과 같이 입력하고 Send를 눌러주세요.
{
"name": "item1",
"price": "100"
}{
"name": "item1",
"price": "100"
}이 경우 FastAPI는 요청을 처리하지만, price가 float로 변해있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
{
"item": {
"name": "item1",
"price": 100.0
}
}{
"item": {
"name": "item1",
"price": 100.0
}
}만약 변환할 수 없는 문자열을 넘긴다면 아래와 같은 경고문구가 뜨고, 처리되지 않는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
{
"name": "item1",
"price": "hello"
}{
"name": "item1",
"price": "hello"
}{
"detail": [
{
"type": "float_parsing",
"loc": [
"body",
"price"
],
"msg": "Input should be a valid number, unable to parse string as a number",
"input": "hello"
}
]
}{
"detail": [
{
"type": "float_parsing",
"loc": [
"body",
"price"
],
"msg": "Input should be a valid number, unable to parse string as a number",
"input": "hello"
}
]
}필수인 항목을 입력하지 않아도 아래와 같은 경고문구가 뜨고, 처리되지 않는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
{
"price": 100
}{
"price": 100
}{
"detail": [
{
"type": "missing",
"loc": [
"body",
"name"
],
"msg": "Field required",
"input": {
"price": 100
}
}
]
}{
"detail": [
{
"type": "missing",
"loc": [
"body",
"name"
],
"msg": "Field required",
"input": {
"price": 100
}
}
]
}5. 요청 본문과 경로 매개변수
요청 본문과 경로 매개변수를 함께 사용할 수 있습니다. 이는 특정 리소스에 대한 정보를 업데이트할 때 유용합니다. 업데이트가 실제로 되었는지를 확인하기 위해 수정하는 코드와 함께 확인하는 코드도 추가하도록 하겠습니다.
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
items = []
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
price: float = 0
@app.get("/item")
async def item_list():
return {"items": items}
@app.post("/item")
async def item_create(item: Item):
items.append(item)
return {"item": item}
@app.get("/item/{item_id}")
async def item_detail(item_id: int):
try:
item = items[item_id - 1]
except IndexError:
return {"error": "Item not found"}
return {"item": item}
@app.put("/item/{item_id}")
async def item_update(item_id: int, item: Item):
items[item_id - 1] = item
return {"item": item}from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
items = []
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
price: float = 0
@app.get("/item")
async def item_list():
return {"items": items}
@app.post("/item")
async def item_create(item: Item):
items.append(item)
return {"item": item}
@app.get("/item/{item_id}")
async def item_detail(item_id: int):
try:
item = items[item_id - 1]
except IndexError:
return {"error": "Item not found"}
return {"item": item}
@app.put("/item/{item_id}")
async def item_update(item_id: int, item: Item):
items[item_id - 1] = item
return {"item": item}이 코드에서 item_detail 엔드포인트는 URL에서 item_id를 받고, 해당 item_id에 해당하는 아이템을 반환합니다. 여기서 해당 index가 없을 경우를 대비하여 예외처리를 해주었습니다.
이 엔드포인트는 URL에서 item_id를 받고, 요청 본문에서 Item 객체를 받습니다. 우선 Thunder Client를 사용하여 POST 요청으로 게시물을 생성하도록 하겠습니다. URL에 127.0.0.1:8000/item/1을 입력하고 Body 탭에서 JSON을 선택하고 다음과 같이 입력하세요.
{
"name": "item1",
"price": 100
}{
"name": "item1",
"price": 100
}제대로 아이템이 생성되었는지 확인하기 위해 GET 요청을 보내보겠습니다. URL에 127.0.0.1:8000/item/1을 입력하고, Send를 눌러주세요. 아래와 같은 응답이 왔다면 정상입니다.
{
"item": {
"name": "item1",
"price": 100
}
}{
"item": {
"name": "item1",
"price": 100
}
}테스트를 위해 2개 이상의 데이터를 입력해주시는 것을 권합니다. 이번에는 PUT 요청을 보내보겠습니다. URL에 127.0.0.1:8000/item/1을 입력하고, Body 탭에서 JSON을 선택하고 다음과 같이 입력하세요.
{
"name": "hello",
"price": 1000
}{
"name": "hello",
"price": 1000
}실제 업데이트가 되었는지 확인하기 위해 GET 요청을 보내보겠습니다. URL에 127.0.0.1:8000/item/1을 입력하고, Send를 눌러주세요. 아래와 같은 응답이 왔다면 정상입니다.
{
"item": {
"name": "hello",
"price": 1000
}
}{
"item": {
"name": "hello",
"price": 1000
}
}6. 요청 본문의 중첩된 모델
Pydantic 모델은 중첩될 수 있어, 복잡한 데이터 구조도 쉽게 처리할 수 있습니다.
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
items = []
class ItemDetail(BaseModel):
description: str
weight: float
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
price: float
details: ItemDetail
@app.get("/item")
async def item_list():
return {"items": items}
@app.post("/item")
async def item_create(item: Item):
items.append(item)
return {"item": item}
@app.get("/item/{item_id}")
async def item_detail(item_id: int):
try:
item = items[item_id - 1]
except IndexError:
return {"error": "Item not found"}
return {"item": item}
@app.put("/item/{item_id}")
async def item_update(item_id: int, item: Item):
items[item_id - 1] = item
return {"item": item}from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
items = []
class ItemDetail(BaseModel):
description: str
weight: float
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
price: float
details: ItemDetail
@app.get("/item")
async def item_list():
return {"items": items}
@app.post("/item")
async def item_create(item: Item):
items.append(item)
return {"item": item}
@app.get("/item/{item_id}")
async def item_detail(item_id: int):
try:
item = items[item_id - 1]
except IndexError:
return {"error": "Item not found"}
return {"item": item}
@app.put("/item/{item_id}")
async def item_update(item_id: int, item: Item):
items[item_id - 1] = item
return {"item": item}이 예제에서 Item 모델은 ItemDetail 모델을 포함하고 있습니다. Thunder Client를 사용하여 POST 요청을 보내보겠습니다. URL에 127.0.0.1:8000/item을 입력하고, Body 탭에서 JSON을 선택하고 다음과 같이 입력하세요.
{
"name": "item1",
"price": 100,
"details": {
"description": "This is an item",
"weight": 10
}
}{
"name": "item1",
"price": 100,
"details": {
"description": "This is an item",
"weight": 10
}
}아이템이 제대로 생성되었는지 확인하기 위해 GET 요청을 보내보겠습니다. URL에 127.0.0.1:8000/item/1을 입력하고, Send를 눌러주세요. 아래와 같은 응답이 왔다면 정상입니다.
{
"items": [
{
"name": "item1",
"price": 100.0,
"details": {
"description": "This is an item",
"weight": 10.0
}
}
]
}{
"items": [
{
"name": "item1",
"price": 100.0,
"details": {
"description": "This is an item",
"weight": 10.0
}
}
]
}연습문제
-
사용자 정보를 저장하는 POST 엔드포인트를 만들어보세요. 사용자 정보는 이름, 이메일, 나이를 포함해야 합니다. Pydantic 모델을 사용하여 데이터를 검증하세요.
-
블로그 포스트를 생성하는 엔드포인트를 만들어보세요. 블로그 포스트는 제목, 내용, 작성자 정보(이름, 이메일)를 포함해야 합니다. 중첩된 Pydantic 모델을 사용하세요.